Ferro Titanium is a ferroalloy composed primarily of iron (Fe) and titanium (Ti). It is typically produced by the aluminothermic reduction of titanium ores in the presence of iron or steel scrap. With a titanium content usually ranging from 30% to 75%, Ferro Titanium plays a crucial role in various metallurgical processes, particularly in the steel and stainless steel industries.
One of the key characteristics of Ferro Titanium is its powerful affinity for oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. This makes it highly effective as a deoxidizer and denitrider during steel production. When added to molten steel, Ferro Titanium binds with these undesirable elements, forming stable compounds that can be easily separated from the metal. As a result, the final steel product becomes cleaner, more ductile, and better suited for high-performance applications.
Another important function of Ferro Titanium is as a grain refiner. In alloy steels, especially those used for aerospace and automotive applications, titanium helps control grain growth during heat treatment and solidification. This results in enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Titanium’s ability to form stable carbides and nitrides also improves wear resistance and high-temperature performance in certain steels.
Ferro Titanium is typically added to steel through wire feeding or in lump form, depending on the specific production method. In continuous casting and ladle refining processes, precise control over titanium content is essential to ensure consistent quality and performance of the final alloy. It is especially useful in low-carbon and ultra-low-carbon steels where controlling interstitial impurities is critical.
In addition to steelmaking, Ferro Titanium is used in the production of superalloys, welding electrodes, and certain powder metallurgy applications. Its corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio make titanium-containing alloys attractive for aerospace components, marine equipment, and chemical processing industries.
From an economic standpoint, Ferro Titanium offers several advantages. Its use improves yield in secondary metallurgy, reduces scrap losses, and enhances the quality of the finished steel, making it a cost-effective addition despite titanium being a relatively expensive element. Moreover, it allows steelmakers to meet stringent specifications required for high-end applications without compromising production efficiency.
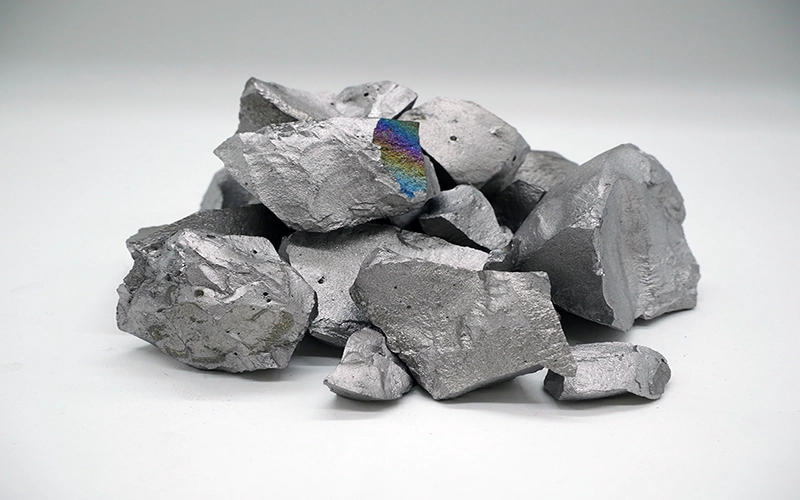

Environmentally, Ferro Titanium contributes positively by helping produce stronger, lighter steels, which in turn can reduce the overall material and energy consumption in various industries. Additionally, the use of recycled titanium scrap in its production supports sustainable resource use.
In conclusion, Ferro Titanium is a versatile and valuable ferroalloy with significant contributions to modern metallurgy. Its role in refining, strengthening, and enhancing the properties of steels and alloys makes it indispensable in industries ranging from construction and transportation to aerospace and defense.
It is used in steelmaking as a cleansing agent for iron and steel; the titanium is highly reactive with sulfur, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen, forming insoluble compounds and sequestering them in slag, and is therefore used for deoxidizing, and sometimes for desulfurization and denitrification.

| Ti | Si | P | S | C | Mn | Size | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70min | 0.6 max | 0.06max | 0.04max | 0.3max | 0.3max | 10-50mm | Russia |
| Ti | Al | C | V | N | Si | Size | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67.44 | 3.84 | 0.24 | 2.27 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 5-50mm | Russia |
© 2013 Vertix Co. All Rights Reserved. Leading Supplier Of Foundry & Metallurgical Materials