Mica is a group of silicate minerals known for their sheet-like structure and remarkable physical properties, including excellent heat resistance, electrical insulation, and the ability to be split into thin, transparent layers. These characteristics make mica an important material in various industrial and commercial applications. The most common types of mica are muscovite (light-colored), biotite (dark-colored), phlogopite (brownish), and lepidolite (lithium-rich).
Mica forms in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, but is most commonly found in pegmatites, which are coarse-grained igneous rocks. It can also be present in schist and gneiss, which are metamorphic rocks. Large deposits of mica are found in countries like India, Madagascar, Russia, China, and the United States. India has historically been one of the largest producers and exporters of high-quality mica.
One of the defining features of mica is its perfect basal cleavage, which allows it to be split into thin, flexible, and almost transparent sheets. These sheets are heat-resistant and non-conductive, making them ideal for use in electrical and electronic industries. Mica is used in capacitors, electrical insulators, circuit boards, and thermal insulation systems. In the past, it was even used in window panes of stoves and furnaces due to its ability to withstand high temperatures.
In the cosmetics industry, finely ground mica is used to add shimmer and sparkle to products like eyeshadows, lipsticks, and nail polishes. Its reflective and refractive properties create a glowing effect on the skin, making it a popular ingredient in highlighters and powders. Mica is also used in paints, plastics, rubber, and construction materials for its durability and decorative appearance.
Despite its usefulness, mica mining—especially in certain regions—has raised ethical concerns. In some countries, particularly India and Madagascar, illegal mining and the use of child labour have been reported, leading to efforts by international organisations and companies to improve supply chain transparency and promote responsible sourcing.
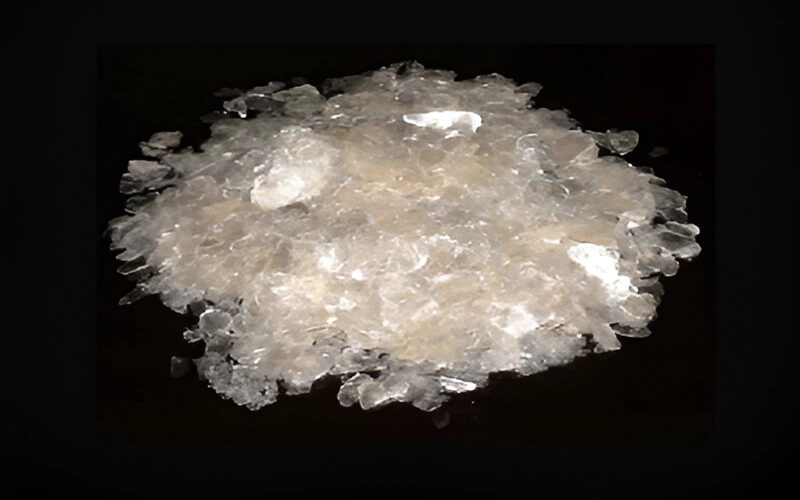

Mica also plays a role in geology and earth sciences, as its presence and characteristics can provide insights into the history and conditions of rock formation. It is relatively stable and can be used to estimate the age of rocks through radiometric dating techniques.
In summary, mica is a versatile and widely used mineral valued for its unique physical properties. Its applications span from industrial electronics to cosmetics, while also raising important social and environmental considerations in its mining and trade.
Mica is stable when exposed to electricity, light, moisture, and extreme temperatures. It has superior electrical properties as an insulator and as a dielectric, and can support an electrostatic field while dissipating minimal energy in the form of heat; it can be split very thin (0.025 to 0.125 millimeters or thinner) while maintaining its electrical properties, has a high dielectric breakdown, is thermally stable to 500 °C, and is resistant to corona discharge..

| Element | SiO2 | AL2O3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | S | LOI | MnO | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent | 47.34 | 34.60 | 2.44 | <0.01 | 0.05 | <0.01 | 0.79 | 9.98 | <0.01 | 4.55 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
© 2013 Vertix Co. All Rights Reserved. Leading Supplier Of Foundry & Metallurgical Materials