Calcined anthracite is a high-carbon material derived from anthracite coal through a process of heating (calcination) at high temperatures, typically between 1200°C and 1500°C. This thermal treatment removes volatile components and moisture, increases carbon content, and enhances physical properties such as hardness, electrical conductivity, and resistance to oxidation. The result is a dense, pure carbon product widely used in various industrial applications.
One of the primary uses of calcined anthracite is in the metallurgical industry. It serves as a carbon additive in steelmaking, where its high carbon content helps improve the carbon composition of steel and other ferrous alloys. It is also commonly used in foundries and ferroalloy production. The material’s low sulfur and ash content make it ideal for these applications, as it minimizes impurities and enhances product quality.
Calcined anthracite is also used in the manufacture of electrodes, particularly in electric arc furnaces and aluminum smelting processes. Because of its excellent electrical conductivity and high temperature resistance, it contributes significantly to energy efficiency and durability in these environments. Additionally, it is used in the production of carbon pastes, blocks, and other carbon-based refractory products that need to withstand extreme thermal and mechanical conditions.
Another important application is in the water filtration industry. Due to its porous structure and high mechanical strength, calcined anthracite is an effective filtering media for removing impurities from drinking water and wastewater. It offers advantages over traditional sand media, such as higher filtration rates and better performance in backwashing cycles.
Calcined anthracite is available in various grades and sizes, depending on the specific application requirements. Its quality is typically measured by fixed carbon content, volatile matter, sulfur, ash, and particle size. A higher fixed carbon percentage usually indicates superior quality, especially for metallurgical and electrode uses.
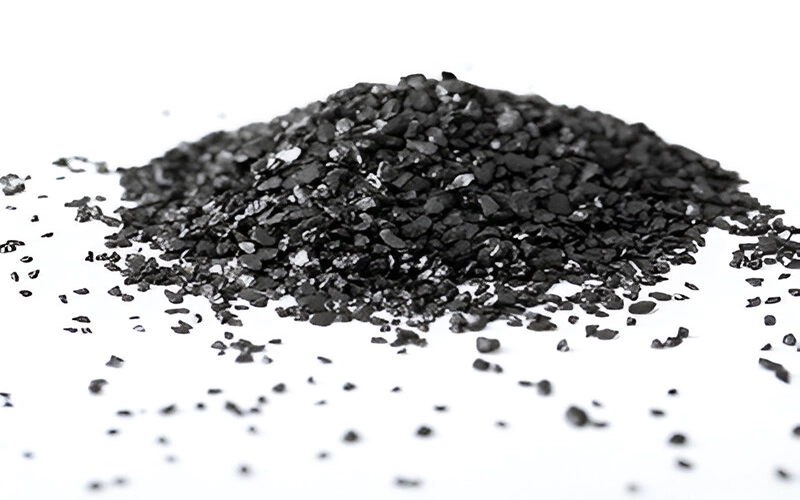

In recent years, the demand for calcined anthracite has increased, driven by the growth of steel production, aluminum industries, and stricter environmental standards requiring cleaner carbon sources. Furthermore, with a global emphasis on reducing emissions, calcined anthracite’s clean-burning properties and efficiency contribute positively to sustainability efforts.
In conclusion, calcined anthracite is a versatile, high-performance material essential across several industrial sectors. Its unique combination of high carbon content, low impurities, and physical resilience makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring purity, durability, and conductivity.
Calcined anthracite is used as a carbon additive in the steel industry or fuel and is mainly used in steel mill ladles, melting, holding and blast furnaces as a recarburizer. It is also used as a substitute for calcined petroleum coke in particular applications.

| Element | FC | Humidity | V.M | S | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent | 95% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 3.4% |
© 2013 Vertix Co. All Rights Reserved. Leading Supplier Of Foundry & Metallurgical Materials