Steel sections are fundamental components in construction and manufacturing, providing strength, durability, and versatility across various applications. These structural elements are produced in various shapes and sizes to meet specific engineering and architectural needs. Steel sections form the backbone of countless infrastructure and industrial projects, whether used in buildings, bridges, machinery, or vehicles.
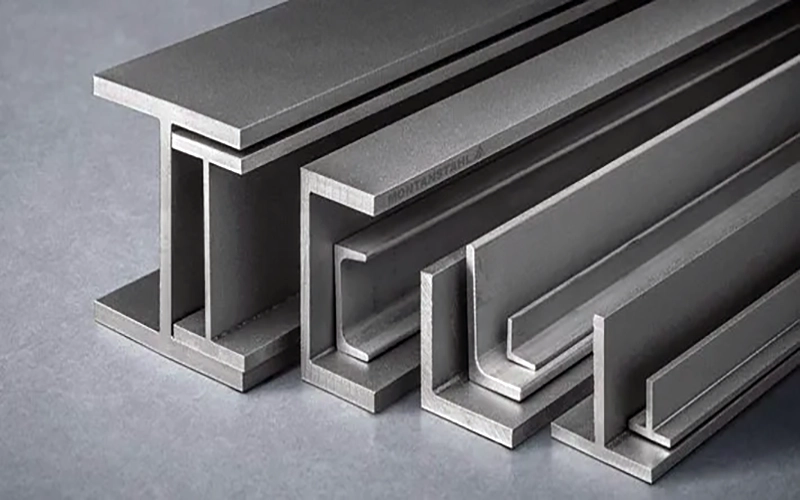
Steel sections are typically categorised by their cross-sectional shapes. The most common types include I-beams (also known as H-beams or universal beams), angles (L-sections), channels (C-sections), T-sections, and hollow structural sections (HSS), such as rectangular, square, and circular tubes. Each type serves a different purpose and offers unique load-bearing characteristics.
For example, I-beams are widely used in construction due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for supporting heavy loads over long spans. Angle sections, with their L-shaped profile, are often employed for bracing and framing, while channel sections are useful in situations requiring a balance of strength and light weight. Hollow sections are particularly favoured for columns and frames, offering excellent resistance to torsion and bending.
Steel sections are produced through hot-rolling, cold-forming, or fabrication processes. Hot-rolled steel sections are manufactured at high temperatures and are commonly used in structural applications due to their robustness and ductility. Cold-formed sections, on the other hand, are shaped at room temperature and are known for their precision and smooth finish, often used in lightweight structures or interior applications.
One of the key advantages of steel sections is their adaptability. Engineers can select specific sections based on load requirements, space constraints, and design preferences. Moreover, steel’s recyclability and long lifespan make it a sustainable choice in modern construction. It is resistant to pests, rot, and fire when treated appropriately, further enhancing its appeal in both residential and commercial building sectors.

In recent years, advances in computer-aided design and structural analysis software have made it easier to optimise steel section usage, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. As urban development continues and infrastructure demands grow, steel sections remain indispensable, delivering the structural integrity and flexibility needed to meet the challenges of modern engineering.
In conclusion, steel sections are more than just metal profiles; they are precision-engineered components that play a crucial role in shaping the built environment. Their variety, strength, and reliability make them a staple in construction and industry worldwide.
Steel sections are structural elements used in construction and engineering, available in various shapes like I-beams, angles, and channels. Known for their strength, durability, and versatility, they support loads in buildings, bridges, and machinery. Steel sections are essential for safe, efficient, and sustainable structural design across many industries.
| Cold Work Tool Steels | Valve Steels | Micro Alloy Steel |
| Hot Work Tool Steels | Carbon Steels | Free Cutting Steels |
| Saw Steels | Carbon Heat Treatable Steels | Welding Filler Materials |
| Plastic Mould Steels | Carbon Tool Steels | Stainless Steels |
| Heat Resistant Steels | Case Hardening Steels | Heat Treatable Steels |
| High Temperature Steels | Spring Steels | |
| Bearing Steels | Nitriding Steels |
| Shape | Dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|
| Round | 12–1000 |
| Square | 40–100, 800 40–160 (RCS) |
| Flat | Thickness 5–60 Min(L×W): 60×140 Max(L×W): 400×1800 |
| Ingot |
(1 ton) S1: 390 S2: 270 H: 1150 (2 tons) S1: 450 S2: 360 H: 1620 (3 tons) S1: 560 S2: 250 H: 1840 |
| Bloom | 230×250 |
| Coil | 12–32 |
| Special shapes | Order-Based |
© 2013 Vertix Co. All Rights Reserved. Leading Supplier Of Foundry & Metallurgical Materials