A gear motor combines a motor and gearbox to efficiently deliver high torque at low speeds.
Couplings are mechanical devices used to connect two shafts at their ends to transmit power
Industrial pumps are mechanical devices designed to move fluids (liquids or gases) through a system
Industrial valves are mechanical devices used to control the flow and pressure of fluids
A gear motor combines a motor and gearbox to efficiently deliver high torque at low speeds.
Gear units are mechanical devices designed to transmit power and motion between machine components through meshing gears. They are essential in many industrial, automotive, and manufacturing applications where controlled speed, torque, and direction of movement are required. A gear unit typically consists of a housing that encases various gear arrangements such as spur, helical, bevel, or planetary gears, depending on the specific application and performance requirements.
One of the primary functions of gear units is to modify the speed and torque of a motor to match the operational requirements of a machine. For example, in applications requiring high torque and low speed—such as conveyors or crushers—gear units reduce the high input speed of a motor to a more manageable output speed while amplifying torque. Conversely, in situations needing high-speed operation, gear units can increase the speed while reducing torque.
There are several types of gear units, each suited to different needs. Helical gear units are known for their smooth and quiet operation due to the angled teeth, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Bevel gear units are used when power needs to be transmitted between intersecting shafts, usually at right angles. Planetary gear units offer high torque density and compact size, commonly used in robotics, wind turbines, and precision machinery. Worm gear units provide significant speed reduction and torque increase in a compact format but tend to have lower efficiency compared to other types.
Gear units are widely used across various industries. In manufacturing, they are found in packaging machines, textile machinery, and conveyor systems. In the automotive sector, they are integral to gearboxes, allowing vehicles to operate efficiently at different speeds. They also play a crucial role in wind energy, where they connect the turbine rotor to the generator, enabling optimal energy conversion.
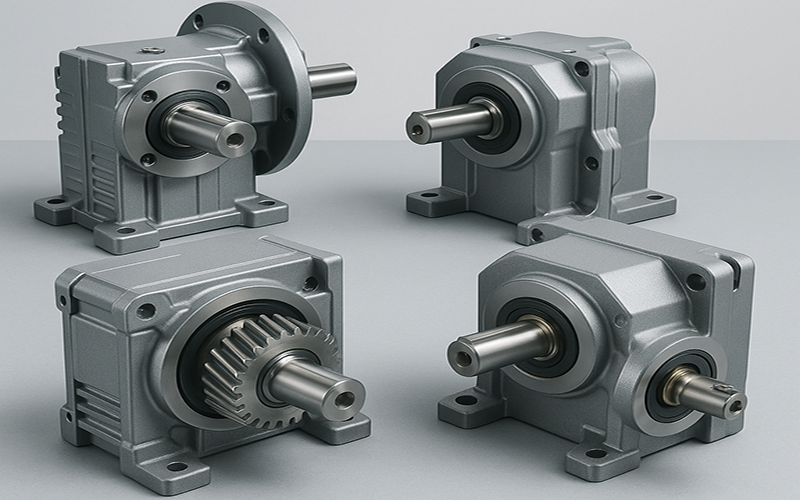
When selecting a gear unit, factors such as load capacity, efficiency, backlash, noise level, and maintenance requirements must be considered. Proper lubrication, alignment, and load distribution are critical for extending the life of gear units and ensuring reliable performance.
In conclusion, gear units are vital components in modern mechanical systems, providing versatility, control, and efficiency. Their wide range of types and applications makes them indispensable in many industries, enabling machines to operate safely and effectively under varying conditions.